In less than two months, the Omicron variant of the Corona virus appeared spread all over the world And the reason Huge number of new infections.
Omicron now accounts for more than 99.5% of new infections in the United States, estimated From the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The nation has mentioned 800,000 new cases per day By mid-January, the number was more than triple what it had been at any previous stage of the pandemic.
Scientists are working overtime to study Omicron. Many questions remain unanswered, but that’s what they’ve learned so far.
Infection and incubation
omicron movements Fast. It spreads rapidly in the population and infection develops rapidly between individuals.
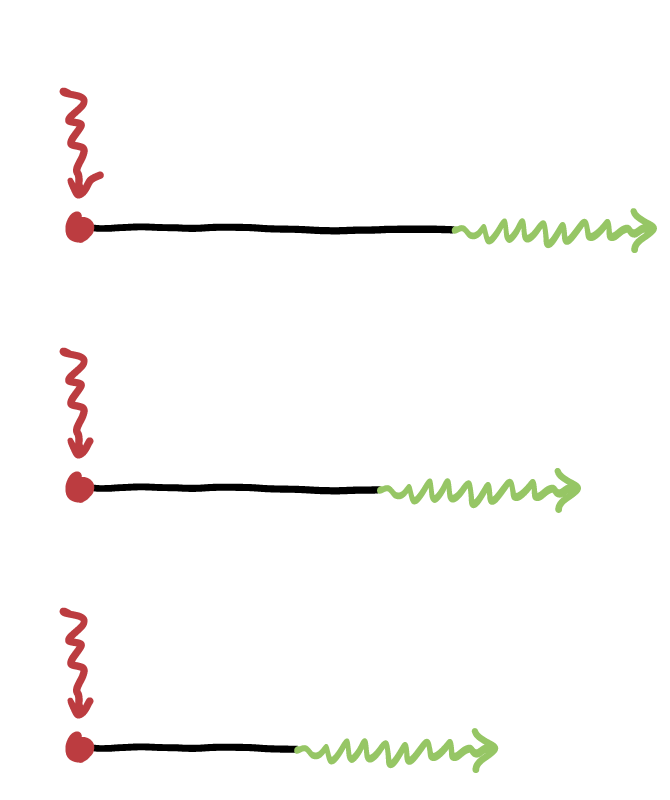
The period between the first time a person was exposed to the virus and the time symptoms appear is known as the incubation period.
Average incubation period
an average
The incubation period
Research indicates that the original version of the coronavirus and its early variants had an average incubation period of about five days. The delta variant appears to move faster, with an average incubation period of about four days. Omicron is faster, with an incubation period of about three days, According to a recent study by the CDC.
Viral burden
The amount of virus that accumulates in the human body is known as the viral load. In general, people are thought to be most contagious when their viral loads are high.
In a recent study From the Alpha and Delta variants, the researchers found that people tend to reach peak viral load about three days after infection and clear the virus after about six days on average.
It remains to be seen if Omicron follows the same pattern. On 1 preliminary study, the researchers found that omicron infection was about one day shorter than delta infection and resulted in a slight decrease in peak viral loads, on average. But the difference may be due to higher rates of pre-existing immunity – as a result of vaccination or previous infection – among people with Omicron. Another research team found that among people vaccinated with sudden infection, Omicron and Delta were produced. Similar levels of infectious viruses.
Other data indicates that Omicron may not function as well as previous variants. Laboratory and animal studies suggest this. It may not be good In infecting the lungs, such as delta, but it can multiply faster in upper respiratory tract.
A variable can also have other unique properties. A small study found that antibodies that are produced after infection with an omicron appear to be Delta protection, but delta infection offers little protection against the micron. If the result is correct, this means that Delta may have trouble finding hospitable hosts anytime soon – and Omicron will likely replace Delta rather than live with it.
Risk
Omicron appears to cause less serious disease than delta disease. On recent studyIn this study, researchers found that people with oomicron infection were less likely to be hospitalized, end up in the intensive care unit, or need mechanical ventilation than those with delta infections.
One possible explanation is that Omicron is less likely to damage the lungs than previous variants. A variant that reproduces primarily in the upper respiratory tract can cause less serious illness in most people. An indication of reduced severity is that unvaccinated individuals are less likely to be admitted to hospital with Omicron than delta.
But Omicron’s apparent restraint can also stem from the fact that it affects vaccinated people much more than Delta. Omicron is able to avoid antibodies produced after vaccination, resulting in more penetrating infectionsBut vaccinators are still protected from the most dangerous diseases. Booster doses of mRNA vaccines are 90% effectiveness Against hospitalization with Omicron, according to the CDC
However, doctors cautioned that while the variant may be milder on average, some patients, especially those who have not been vaccinated or who have compromised immune systems, can become seriously ill from oomicron infection. It is too early to say whether violations of Omicron could lead to this. long covid.
testicles
Because Omicron reproduces very quickly and the incubation period is very short, there is a narrower window in which infection is detected before people begin transmitting the virus.
At the start of the pandemic, people were advised to get a rapid test five to seven days after potential exposure to the virus. Given Omicron’s shorter incubation period, many experts now recommend a rapid test after two to four days of potential exposure. (They also recommend at least two quick tests, about a day apart, to increase your chances of detecting an infection.)
Experts said that people who are being tested to reduce the risk of transmitting the virus to others, for example at an upcoming meeting, should get tested as close as possible to the event itself.
There is still controversy as to whether Rapid antigen tests may be less sensitive for omicron than other variants. PCR tests are more sensitive The tests are rapid, which means they are likely to detect the virus earlier in the course of infection, but take longer to return results.
The new rules of isolation
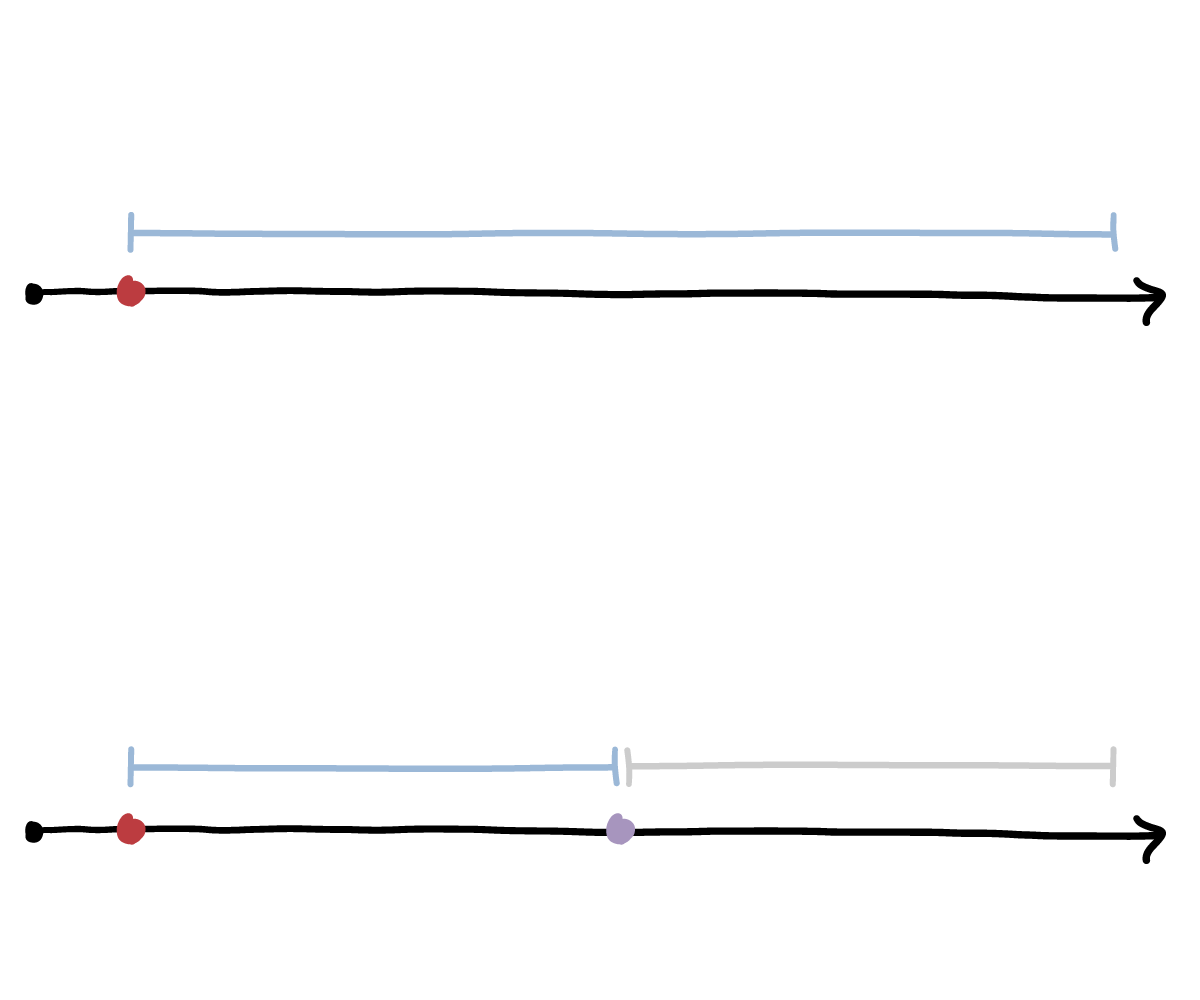
The Center for Disease Control recently Relax his isolation guidelines For people infected with the virus. Previously, the agency recommended that people who tested positive for the virus or showed symptoms of Covid-19 should remain in isolation for 10 days.
a new instructions He says infected people can be discharged from isolation after five days if they do not show symptoms or if symptoms disappear and they are free of fever. People must wear appropriate masks for an additional five days when they are near other people.
positive test
(or symptoms)
avoid travel,
wear a mask
positive test
(or symptoms)
positive test
(or symptoms)
positive test
(or symptoms)
The agency said These changes are required Data suggest that transmission of the virus may occur one or two days before symptoms appear and two or three days after.
But scientists note that some people can be contagious for longer than that, and Some criticized the agency Not recommending that people receive a negative result in a rapid test before ending periods of isolation.
The agency later updated its guidelines to note that people who want to get tested should have a rapid antigen test “at the end” of the five-day isolation period, but they couldn’t recommend it officially.

“Wannabe internet buff. Future teen idol. Hardcore zombie guru. Gamer. Avid creator. Entrepreneur. Bacon ninja.”