
Floating solar parks? What are they and why are they increasingly sought after?
Floating solar parks are becoming an increasingly popular option for countries that want to accelerate decarbonisation.
How do floating solar farms work?
Since it is an option sought by countries wishing to invest in renewable energies, it certainly has great advantages and possibly some disadvantages.
In Portugal there are some installations of this type, starting at Alto do Rabadão, Barragem do Alqueva and briefly at the Cabril Dam, Zêzere River.
What is floating solar park?
In this infrastructure, water mirrors are used to assemble photovoltaic panels, thus serving as an alternative to ground-mounted photovoltaic panels.
This installation came with the need to discover new ways to produce cleaner energy, being a relatively recent concept.
The first floating solar garden appeared in 2008, in countries such as China, Japan, the United Kingdom, etc., and more recently in Portugal.
Video – Alto do Rabadao Floating Solar Park
Floating solar parks in Portugal
In Portugal we already have two photovoltaic parks of this type in operation.
The first, which is considered the pilot project, was in Alto do Rabagao, about 7 years ago. There, on the Rapagau River, 840 floating solar panels have been installed in the dam’s reservoir, with a capacity of 220 kW!
However, after the successful commissioning of this pilot project, the largest floating solar park in Europe was opened in July 2022, a project installed in the Alqueva Dam, consisting of 12,000 photovoltaic panels. Equivalent to 4 hectares, with an installed capacity of 5 MW, and an annual production of 7.5 GWh.
The next project will be born in the Cabriel Dam, on the Zizer River, on an area of about 33 hectares. Which will translate into a total power of between 33 and 40 MW.
second World Bank reportWhere the Sun Meets the Water: Floating Solar Market Report In the next two decades there will be a boom in this type of installation.
These infrastructures translated into numbers, in 2020 the total power of these infrastructures is 3GW, and in 2025 this power is translated into 10 GW!
But then, how do they work?
They are nothing more than plants to produce energy through solar photovoltaic energy, but they are installed in the water (floating structures).
They can be found in ponds, lakes, reservoirs or dams. Ideal in areas with large surface areas and calm waters.
They are installed on a floating structure, waterproof, easy to access and maintain.
Solar panels in this type of installation must be moisture and dust resistant and well protected from the effects of water.
The material used in the floating structure?
The hull’s buoyancy is made mostly of polyethylene, and is capable of supporting up to 2.5 times its own weight.
However, studies have been developed to create new options for sustainable materials that are able to float. The Amorim Group’s i.Cork factory tests the most sustainable material known, Portuguese cork.
This floating structure is coated with magnesium alloy, which is highly resistant to corrosion.
The electricity produced by the photovoltaic panels is then transmitted to a central inverter before reaching electrical equipment on land via submarine cables.
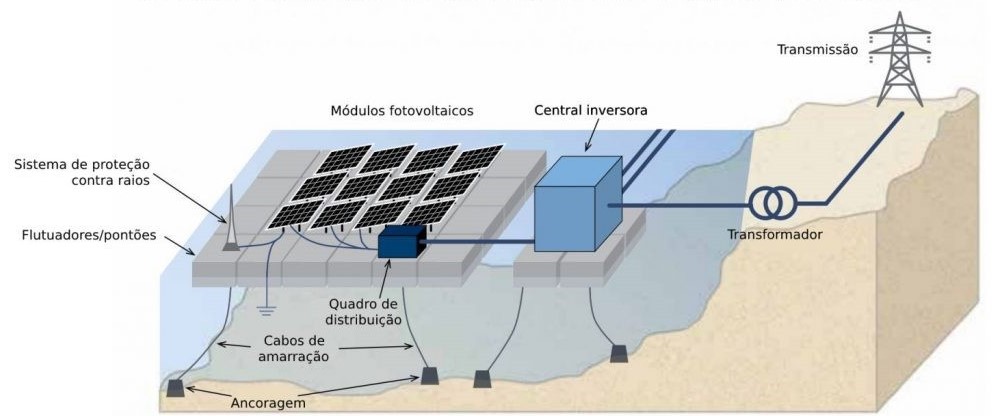
Then the power is sent from the inverter to the converter, which reduces it, and then it is fed to the transmission system that leads to the final consumer.
Another interesting feature of these floating platforms is that they can be easily rotated both horizontally and vertically, thus tracking the movement of the sun. To do this, they use some energy, but they don’t need a large mechanical device, as is the case with their terrestrial equivalents.
Doing the math, according to experts’ calculations, outfitting a floating solar garden with a solar circulation system has minimal cost, with a significant energy gain, between 15% and 25%!
From what we’ve written up to this point, it should be noted that this type of infrastructure has several advantages.
The main reason is the lack of land on which to build, as it takes advantage of the ‘unused’ space above the water, and allows for higher energy production and a lower maintenance cost. But it also has some advantages!
The largest floating solar PV project in Europe was born in Alqueva
The main advantages and disadvantages of floating solar power
Advantages of floating solar power
- Doesn’t take up land space: At a time when soil and land resources are becoming less available, making use of the space occupied by water is an asset.
- Increases electricity production: Since it is water-based, this allows PV panels not to overheat, thus improving their efficiency when overheating. It has been shown that electricity production can increase by about 11% (tests were carried out at the Floating Solar Park in Hyogo, Japan).
- It helps to reduce the evaporation of water and the appearance of algae: when placed above the water, it creates shade, thus preventing partial evaporation of the water. Shade also helps reduce algae blooms.
- Ease of maintenance: Since the structure floats on water, there is less dust pollution in the air, and therefore less dirt on the panels. There is even a maintenance driveway to access the solar panels.
- No shadows limiting electricity production: The fact that it is in the center of the water mirror means that there will be no shadow over the solar panels, thus increasing their output, due to the higher exposure to sunlight. A condition that does not occur when placed in terrestrial locations.
Disadvantages of floating solar power
- Complex mounting system: In order for the floating solar garden to last for a long time, it requires complex mounting systems. Systems that can withstand water for more than 25 years, so the fasteners must be resistant to corrosion from water and the load that will be placed on them.
- High costs: Compared to a ground solar park, this type of solar park can cost 20-25% more. This cost increase is due to the use of buoys and anchor systems. Also note whether or not the site is windy. Because places with strong winds and waves require more effort and resistance than the floating platform.
- Limited Technology: It is not a suitable technology for all purposes. It’s ideal for communities or businesses, never for an individual. For the private individual, the best option is solar panels on your roof or other ground-based structure.
- Impact on aquatic life: By preventing sunlight from penetrating into the water, it will harm the aquatic wildlife in the area where the solar park is set up. In addition, anchor cables can still injure animals. Therefore, the ideal option is to install them in artificial lakes or reservoirs with few wild animals.
Countries with floating solar parks
Still unusual in Europe, in Asia we find more installations of this type. This fact is due to the high population density, scarcity of land and the predominance of rugged terrain (mountains).
Countries such as China, India and South Korea lead the table with the highest investment in floating solar power (about two-thirds).
There is China’s largest floating photovoltaic power plant, in Dezhou Province – Solar Valley, with a capacity of 320 MW, on top of a fish farm.
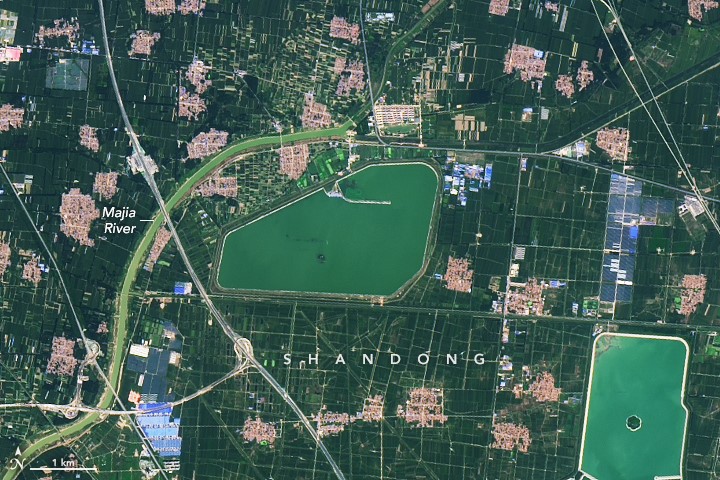
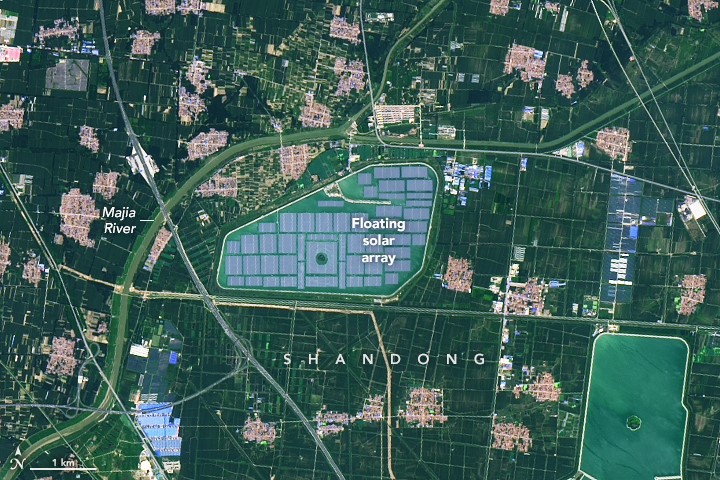
Video – Valley Solar floating photovoltaic power plant
India does not want to be left behind and will soon finish its 600MW floating park in Narmada River.
Future potential of floating solar parks
Researchers say that if 10% of the world’s large water reservoirs were covered with solar panels, they would produce 4,000 gigawatts, which is the equivalent of all power plants using fossil fuels.
If we take the case of the United States, putting solar panels on a quarter of the 24,000 existing water tanks would produce about 10% of the electricity they currently generate.
Present The installed capacity of floating parks around the world is 3GW, values that are not competitive with 700 gigawatts for terrestrial systems. But in our water reservoirs we have the largest space for expanding renewable solar energy, because adding up the area of all the reservoirs, we have an area the size of France.
Everything indicates that the future will be marked by the allocation of new floating garden projects around the world. Since there are still goals to combine this type of photovoltaic production with wind production.

“Wannabe internet buff. Future teen idol. Hardcore zombie guru. Gamer. Avid creator. Entrepreneur. Bacon ninja.”

