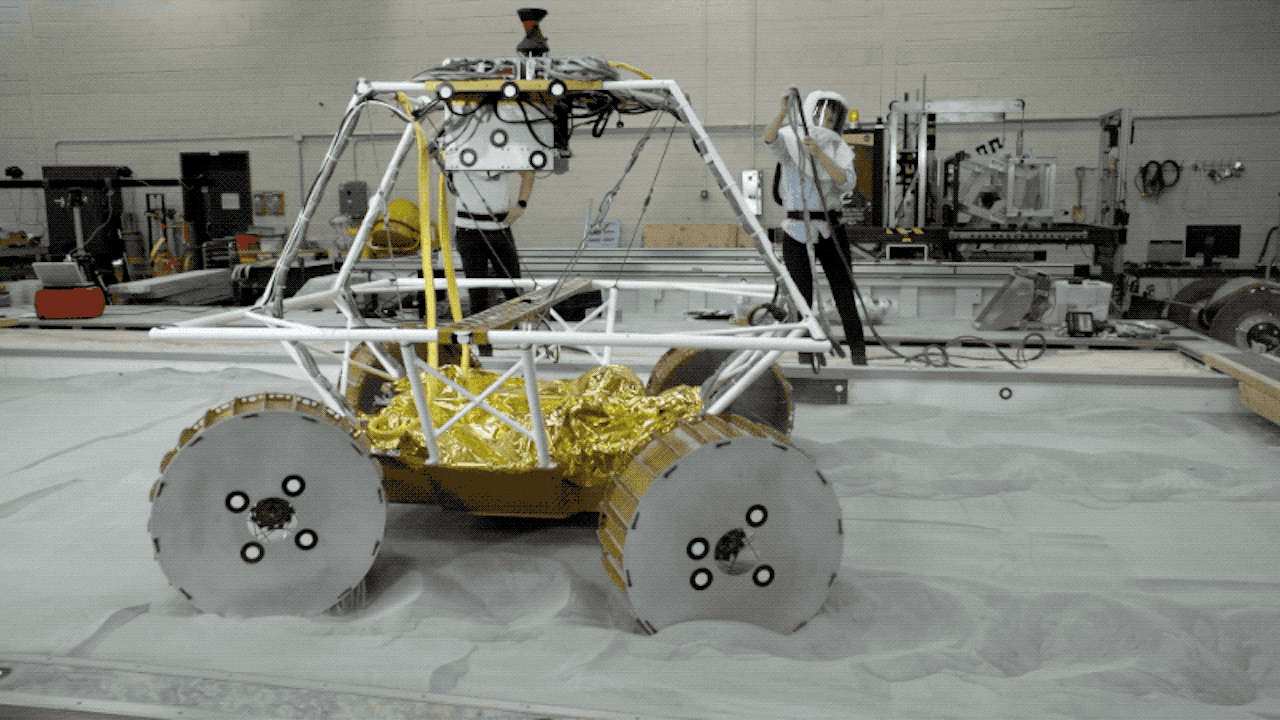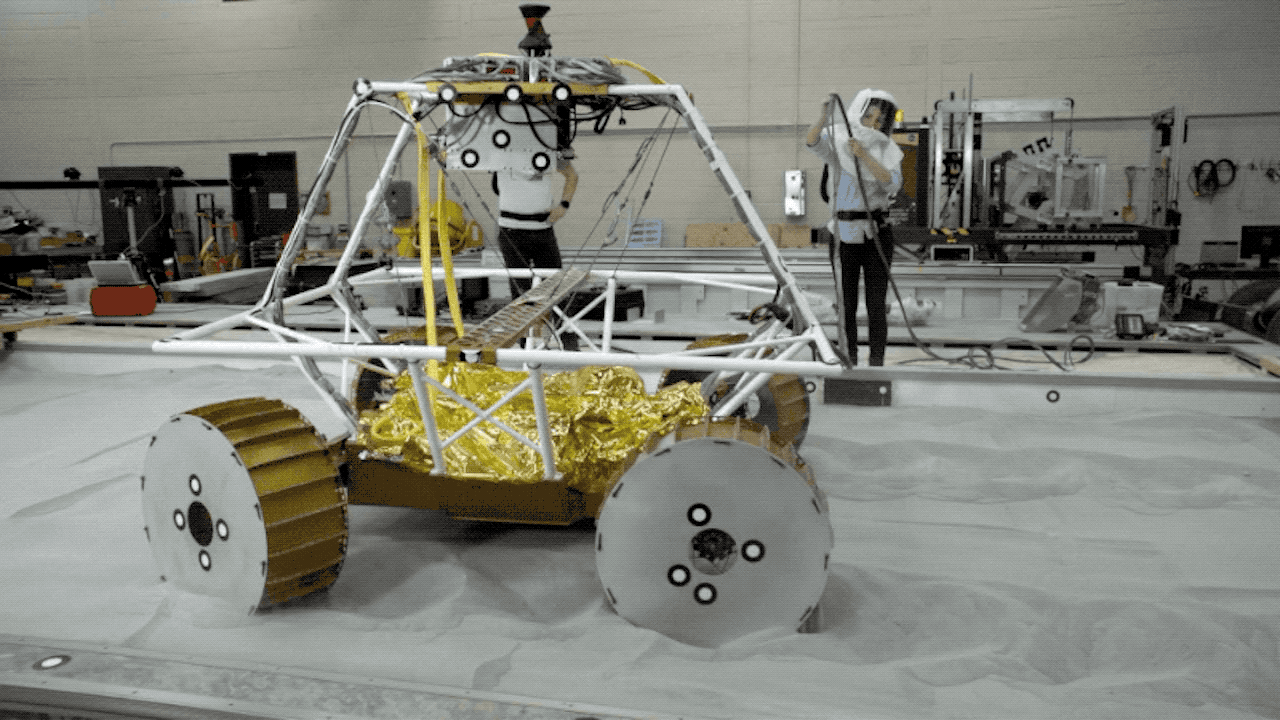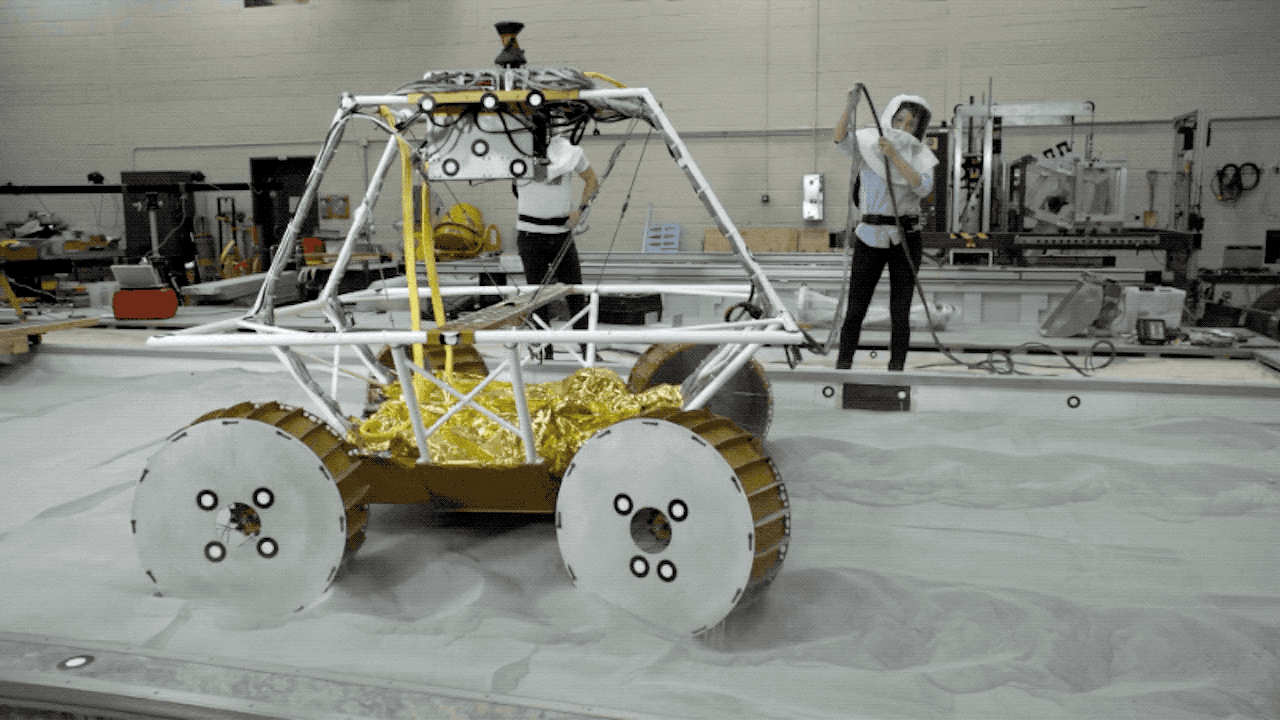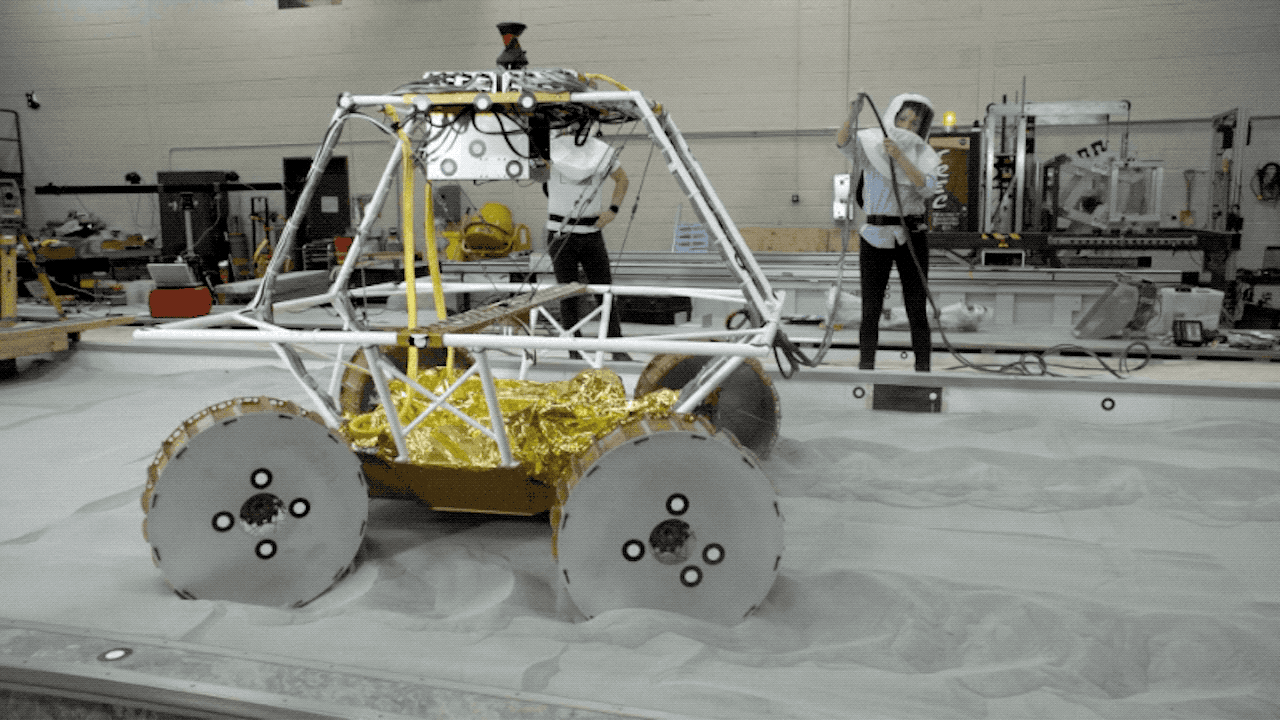
After Mars, where NASA has already placed many rovers, it is time for the US space agency to return to the moon, meaning that NASA plans to send the first mobile robot to a natural satellite in late 2023.
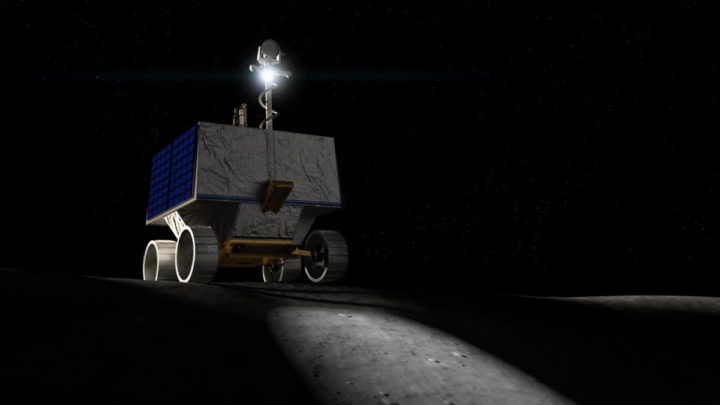
VIPER is a rover whose mission is to search for water and other resources both on the surface and underground.
Rover VIPER is the moon exploration robot from the Artemis mission
NASA already has plans to send a VIPER (Polar Exploration Volatile Module) to lunar soil in order to collect data in the Antarctic that will help the agency locate everything that might one day be useful to future human explorers.
This rover is part of the Artemis program and NASA's desire to return to the place It made history in space more than 50 years ago. An intriguing fact is that this vehicle was the first to bring headlamps to illuminate the road in exploring permanently shaded lunar regions.
The concern for these dark areas, as well as the potential for storing water, is the absence of sunlight for billions of years. Incidentally, it is referred to as one of the coldest points in the solar system. Hence, this lunar craft will have to challenge its capabilities, in addition to working on solar energy. It will experience extreme temperatures ranging from -153 ° C to 123 ° C when the sun hits the moon.
VIPER data has the potential to assist our scientists in determining the exact locations and concentrations of ice on the Moon and will assist us in assessing the environment and potential resources in the Lunar South Pole in preparation for Artemis astronauts.
This is yet another example of how robotic science missions and human exploration go hand in hand, and why both are needed as we prepare to establish a sustainable presence on the Moon.
Lori Glaze, director of the Department of Planetary Sciences at NASA in Washington, explained.
NASA is seeking to explore places where water ice is found, which deep space explorers in the future could use as porous air and rocket fuel.
So, instead of taking these resources from the earth, they can already be there and make the missions more sustainable.
From the Earth to the moon
VIPER will travel aboard the Griffin Lunar Module. Once the robot reaches the moon, it will explore the craters for three lunar days (100 Earth days). To do this, the rover will use a specialized set of wheels and suspension system to cover a variety of slopes and soil types.
In addition, it will require four tools: a percussion drill (Trident) and three spectrometers (MSolo, Nirvss, and NSS).
Astrobotic is the company responsible for launching, transiting and delivering VIPER to the surface of the Moon. The company is part of the NASA program, Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS), Those who hire transport services capable of sending small sums.Landing“Robotic lunar vehicles and exploration to our natural satellite.
NASA has invested 350 million euros in this mid-sized rover and the current value of Astrobotic's contract to deliver VIPER to the Moon is around 185 million euros.
VIPER will be the most capable robot NASA has ever sent to the surface of the Moon and will allow you to explore parts of the Moon that we haven't seen before. The rover will teach us about the origin and distribution of water on the moon and prepare to gather resources 386,000 kilometers from Earth that can be used to safely send astronauts further afield, including Mars.
Sara Noble, a software scientist at NASA headquarters, concluded.
The Artemis program includes sending robots and humans to explore the moon like never before.
Read also:

“Coffee trailblazer. Social media ninja. Unapologetic web guru. Friendly music fan. Alcohol fanatic.”